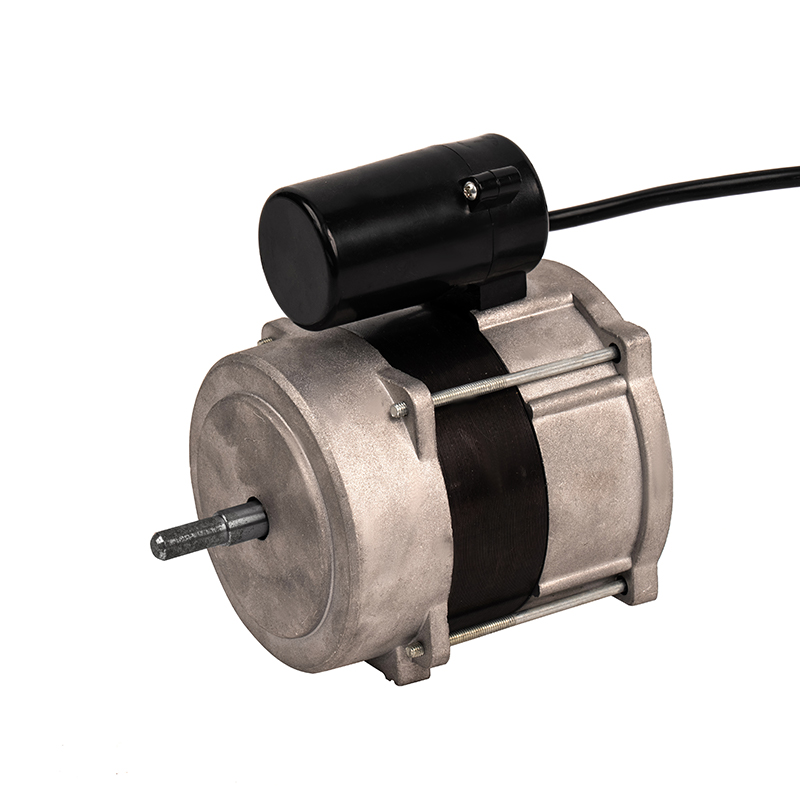
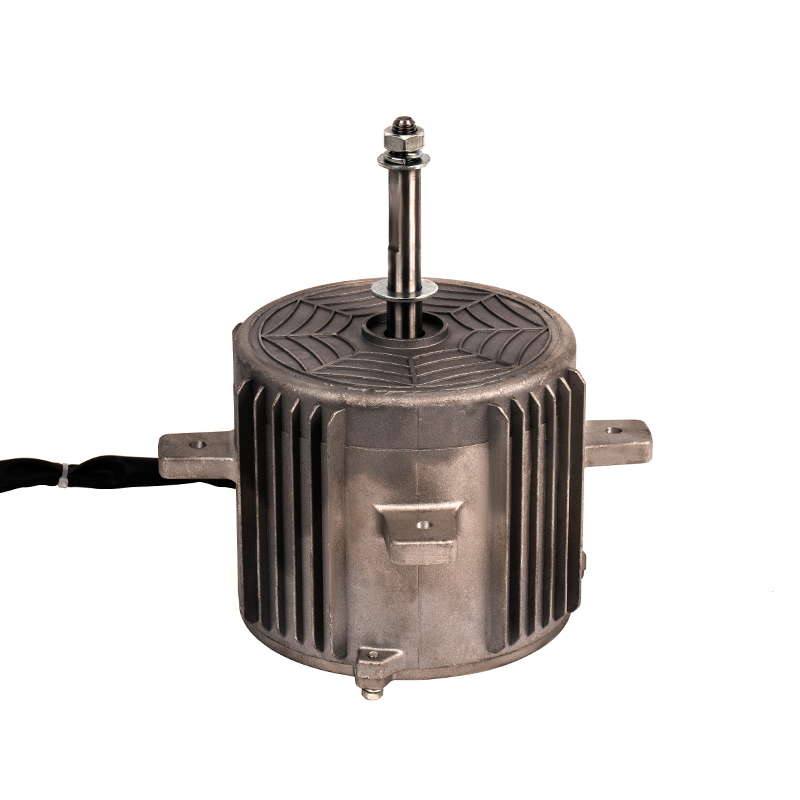
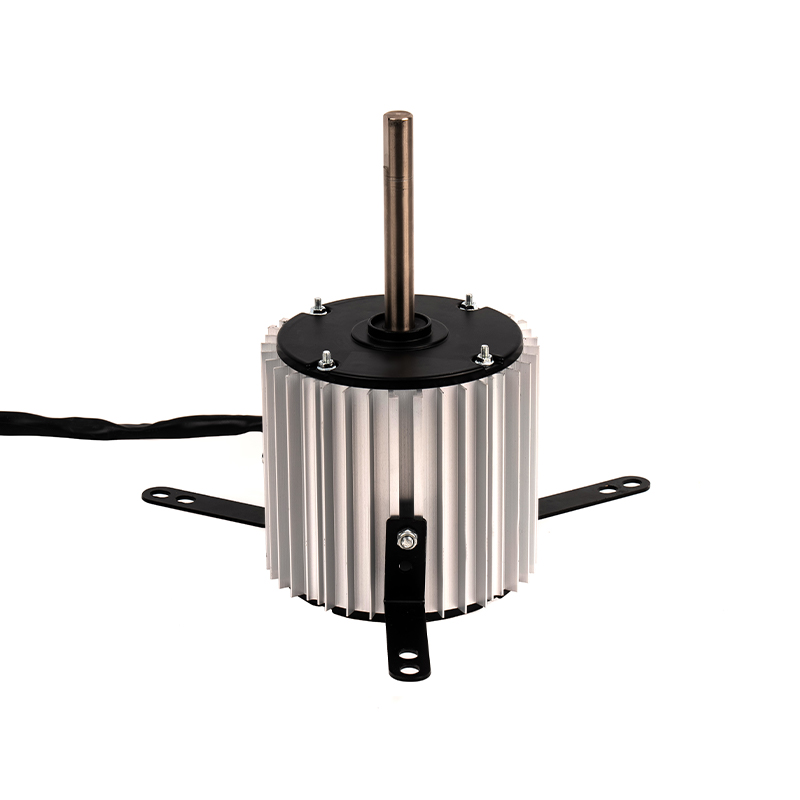
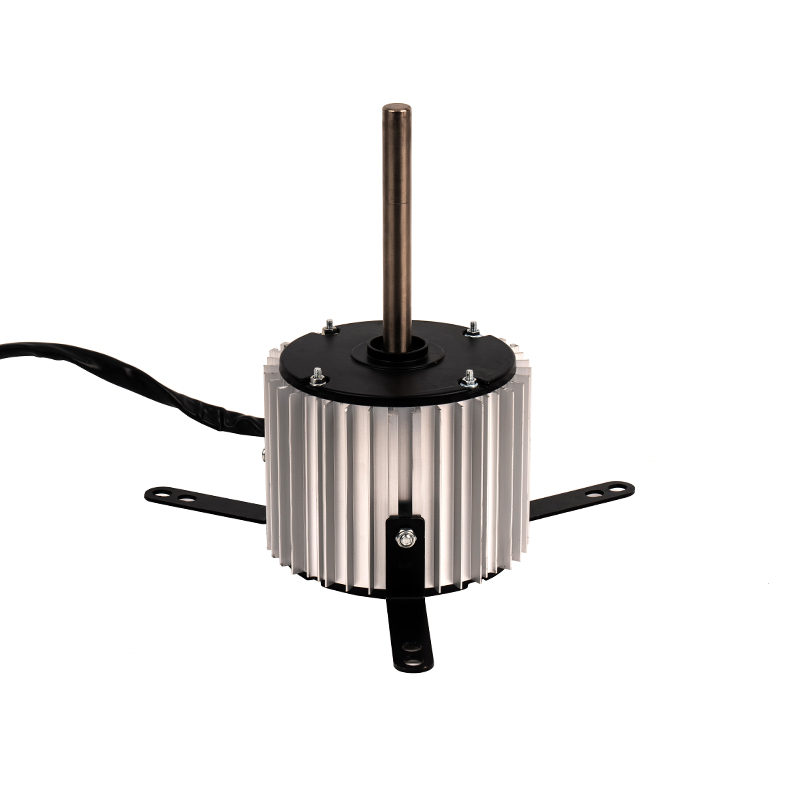
Over time, industrial motors, including aluminum shell cold air AC motors, accumulate dust, dirt, and debris, especially in environments with high levels of particulate matter or moisture. These contaminants can obstruct airflow, reducing the motor’s cooling efficiency and causing it to overheat. The aluminum shell, while resistant to corrosion, can still suffer from external debris buildup that obstructs its cooling fins, which are essential for dissipating heat. To maintain optimal motor performance, it is critical to implement a regular cleaning schedule. This may involve using compressed air to blow out dust from vents, fans, and cooling fins, or a soft brush to remove particulate buildup. For motors located in particularly dirty or dusty environments, cleaning may need to occur more frequently. An external cleaning process not only helps maintain airflow but also provides the opportunity for users to inspect the motor for signs of wear or damage.
The aluminum casing of cold air AC motors provides essential protection against environmental elements, such as moisture, dust, and minor physical impacts. However, regular inspection of the aluminum shell for any signs of physical damage is vital. The casing can still suffer from corrosion if exposed to harsh chemical vapors, salty air, or extreme moisture levels over time, even though aluminum is known for its corrosion resistance. Cracks, dents, or abrasions in the aluminum shell can compromise the structural integrity and cooling properties of the motor. These damages can lead to more serious internal motor issues, such as electrical short circuits or mechanical failures. Periodically inspect the motor’s shell for physical damage, particularly around mounting points, ventilation areas, and areas exposed to heavy handling or vibration. Prompt repairs to any damage can prevent further deterioration and ensure the motor maintains its protective function.
Bearings play a crucial role in the smooth operation of any AC motor, and aluminum shell cold air AC motors are no exception. Bearings are responsible for reducing friction between moving parts, such as the rotor and the stator, allowing for smooth and efficient rotation. Without adequate lubrication, the bearings can wear down, causing increased friction and heat generation, which can lead to premature motor failure. Depending on the motor's usage and design, the bearings may require routine lubrication to maintain proper function. In motors with sealed bearings, lubrication may be unnecessary, but motors with open bearings require regular checks for oil or grease levels and replenishment. Lubrication intervals can vary based on the operating conditions—motors operating in high temperatures, dusty environments, or with heavy loads may require more frequent lubrication. Always use the lubricant recommended by the manufacturer, as using the wrong type can lead to inadequate performance and damage to internal components.
Regular monitoring of motor performance is essential for detecting potential issues before they lead to failure. Early signs of motor stress, such as unusual noises (grinding, screeching, or rattling), can indicate problems with the bearings, shaft alignment, or other moving parts. Aluminum shell cold air AC motors are designed to run within a specific temperature range, and consistent monitoring helps ensure the motor operates efficiently. An increase in temperature beyond normal levels could point to a blockage in the ventilation system, an issue with the bearings, or an electrical fault. Vibration analysis can also be performed to detect imbalances or misalignment in the motor's components, which could reduce efficiency and cause long-term damage if left unaddressed.


 English
English عربى
عربى ++86 13524608688
++86 13524608688












