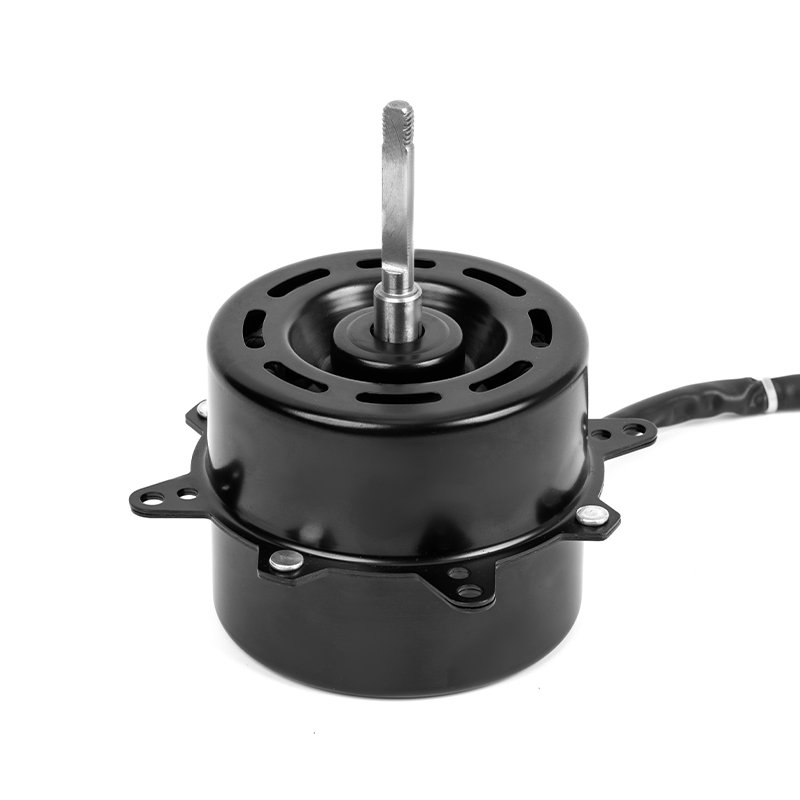
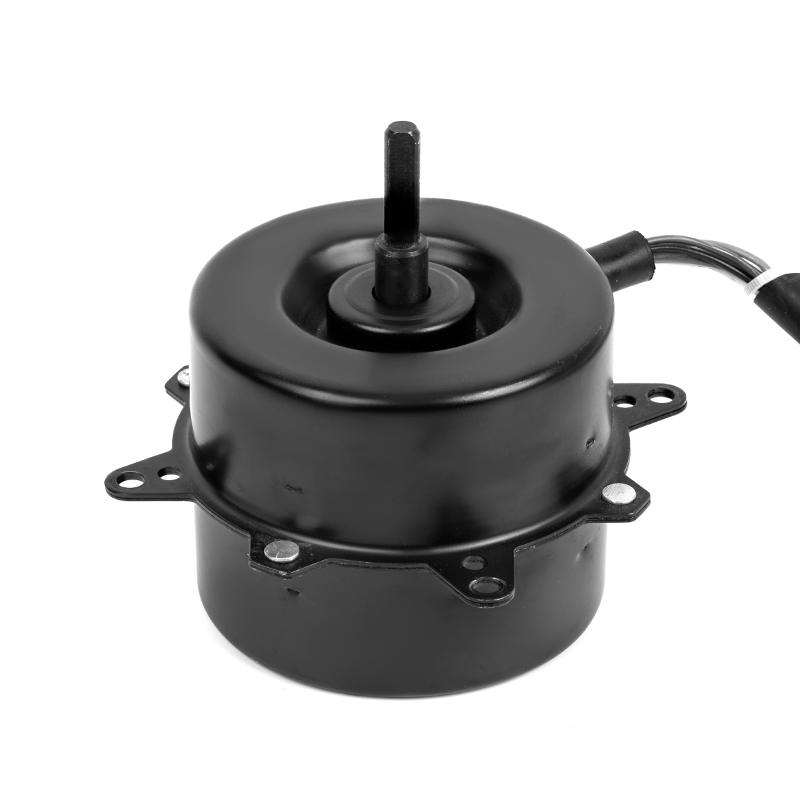
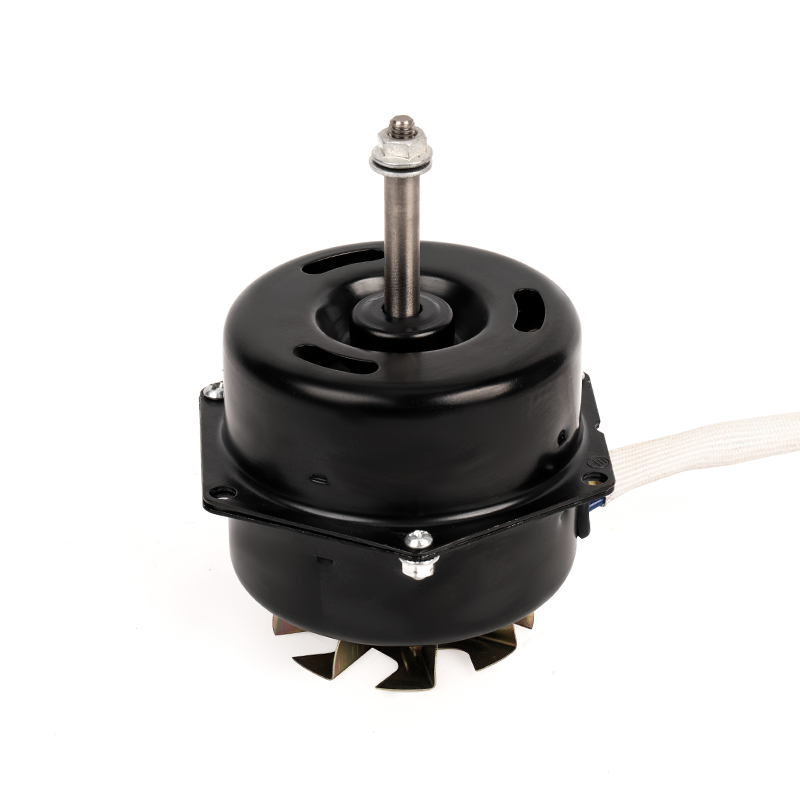
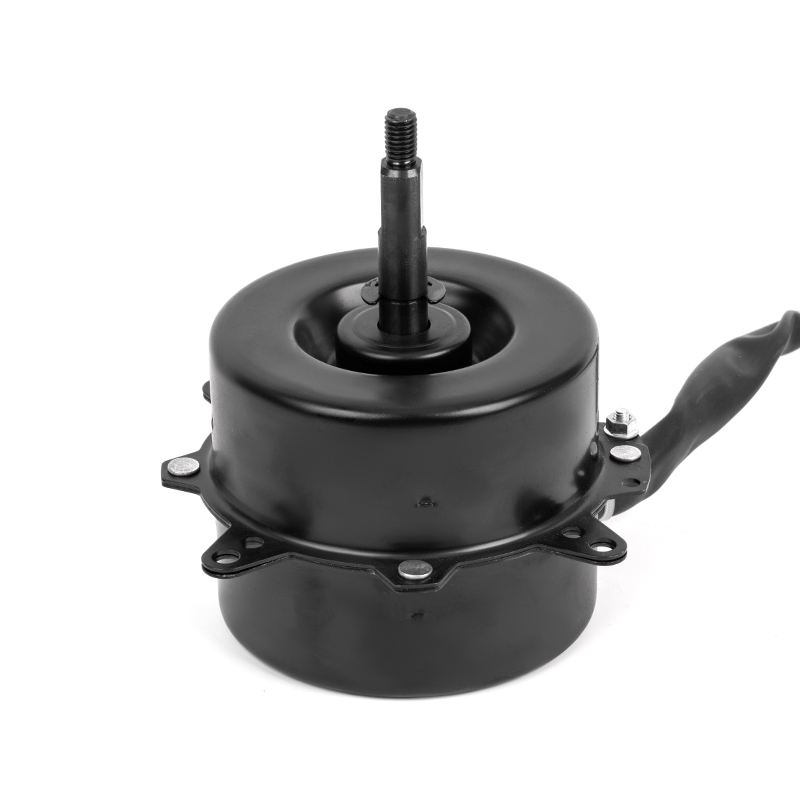
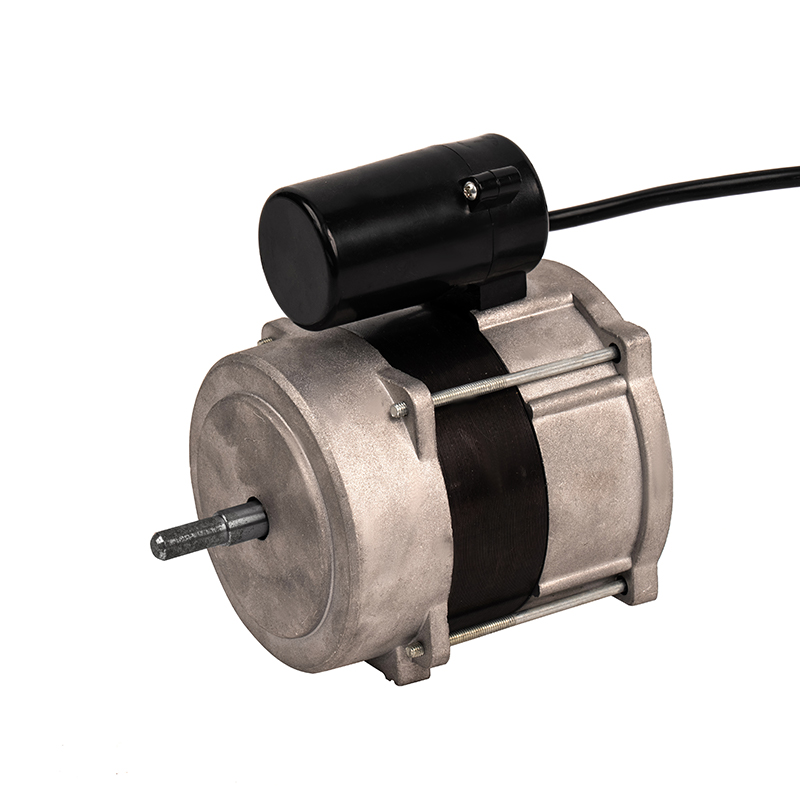
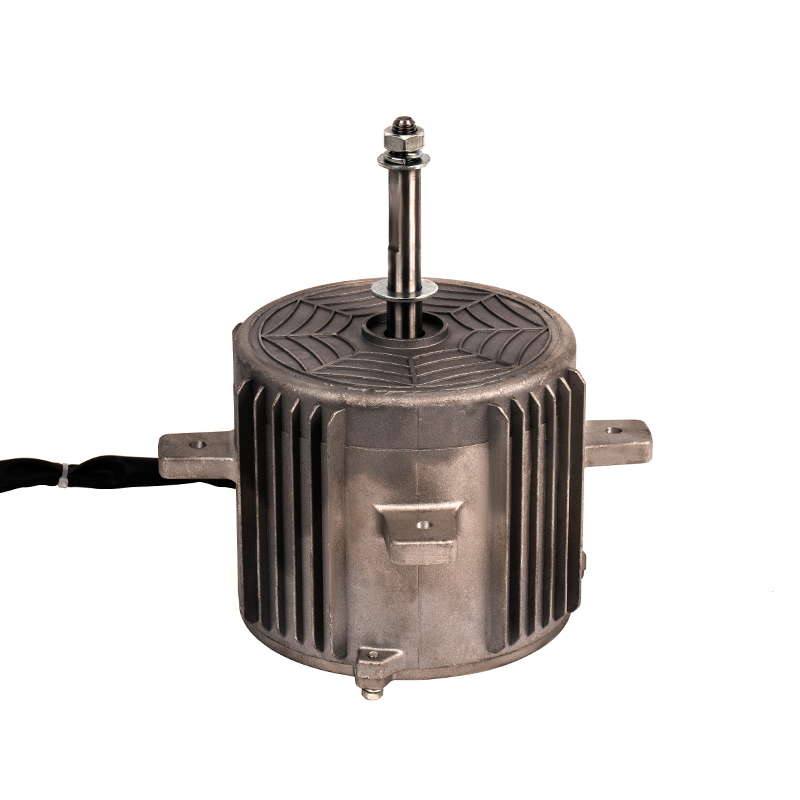
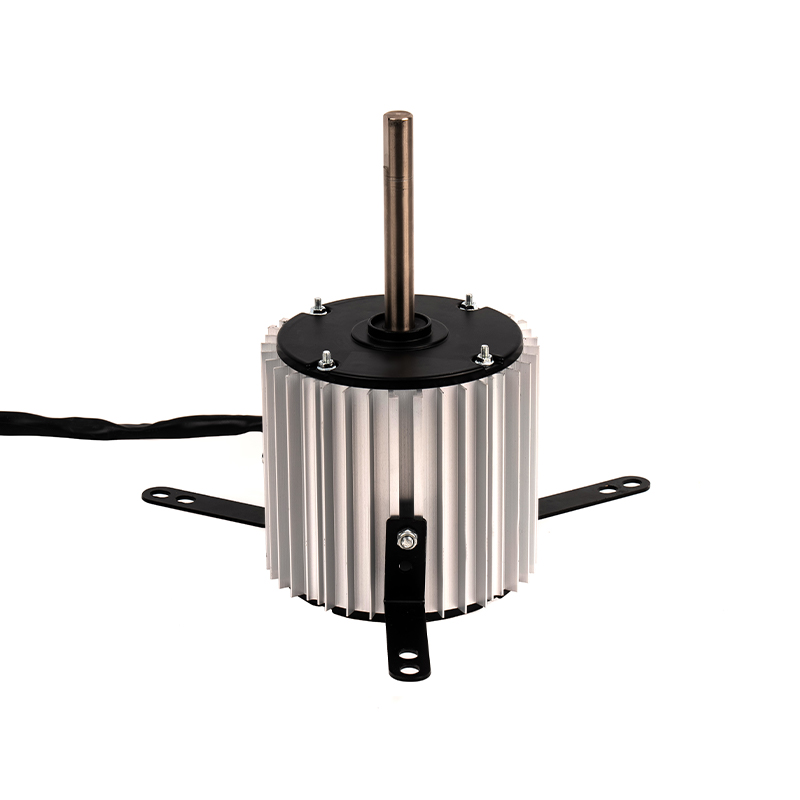
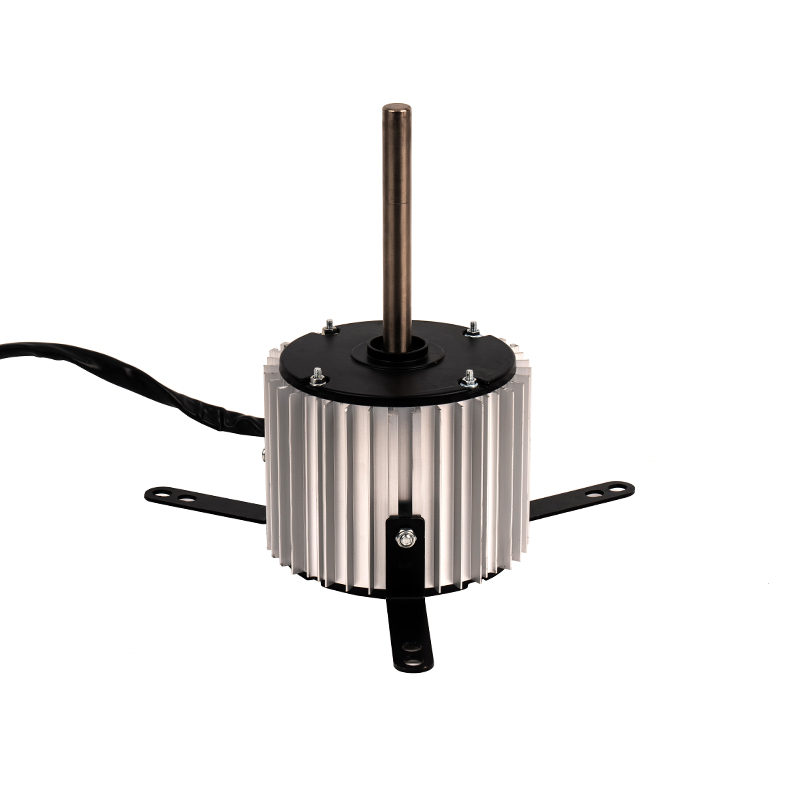
Aluminum shell AC motors are designed with efficient heat dissipation properties due to the material’s thermal conductivity. However, improper ventilation or clogged vents can severely hinder heat dissipation, leading to excessive motor temperatures. Prolonged overheating can cause the insulation to degrade, resulting in electrical short circuits or the motor's failure. Prevention: Proper installation is critical—ensure sufficient space around the motor for airflow. Regularly clean and maintain ventilation areas to prevent debris, dust, or dirt buildup that could obstruct the motor’s cooling efficiency. In environments with high ambient temperatures, installing additional cooling systems, such as external fans or air conditioning, can help maintain the motor's optimal temperature range. Using motors rated for higher temperature environments or ensuring the motor is placed in a climate-controlled area can also be effective.
While aluminum naturally has a higher resistance to corrosion than many metals, the aluminum shell can still succumb to corrosion if exposed to prolonged moisture, high humidity, or corrosive chemicals. This is particularly concerning for motors used in environments like industrial kitchens, coastal regions, or places with frequent chemical exposure. Corrosion of the aluminum casing can compromise the motor’s integrity and cause failures in its function. Prevention: Use aluminum motors with anodized coatings or protective finishes designed to resist corrosion, particularly in harsh environments. Consider using seals and gaskets around motor housing to prevent moisture ingress. If the motor will be used in extremely corrosive environments, choosing a more corrosion-resistant material, such as stainless steel, or a more robust protective coating will enhance the motor’s longevity. Regularly inspect the shell for signs of wear or corrosion, and take proactive steps to maintain the protective layer.
Bearings are integral to the smooth operation of an AC motor, supporting the rotor and reducing friction. However, over time, bearings can wear out due to factors such as insufficient lubrication, dust or debris ingress, or exposure to excessive loads. Worn-out bearings may result in vibrations, noise, overheating, or even catastrophic motor failure. Prevention: Regularly inspect and lubricate bearings according to the manufacturer's recommendations to ensure smooth operation. Pay attention to early signs of bearing failure, such as unusual noises or vibrations, and replace bearings before they deteriorate completely. Protect bearings from contaminants by using seals or filters to prevent dust, dirt, or moisture from entering the motor housing. For high-load or high-speed applications, ensure the bearings are rated for such conditions, and replace them at recommended intervals to ensure optimal performance.
Aluminum shell AC motors, like all electrical motors, are vulnerable to damage from electrical surges or voltage spikes, which can occur due to lightning strikes, power grid fluctuations, or the starting of large electrical equipment nearby. These surges can damage sensitive electrical components, such as the windings, capacitors, or the motor’s control circuit, leading to malfunction or complete failure. Prevention: To safeguard against power surges, it’s crucial to install surge protection devices such as voltage suppressors, circuit breakers, or surge arresters at the point of power entry. These devices protect the motor from sudden voltage spikes that can cause irreversible damage. For systems prone to power fluctuations, consider integrating power conditioning equipment or using motors with built-in surge protection capabilities.


 English
English عربى
عربى ++86 13524608688
++86 13524608688












