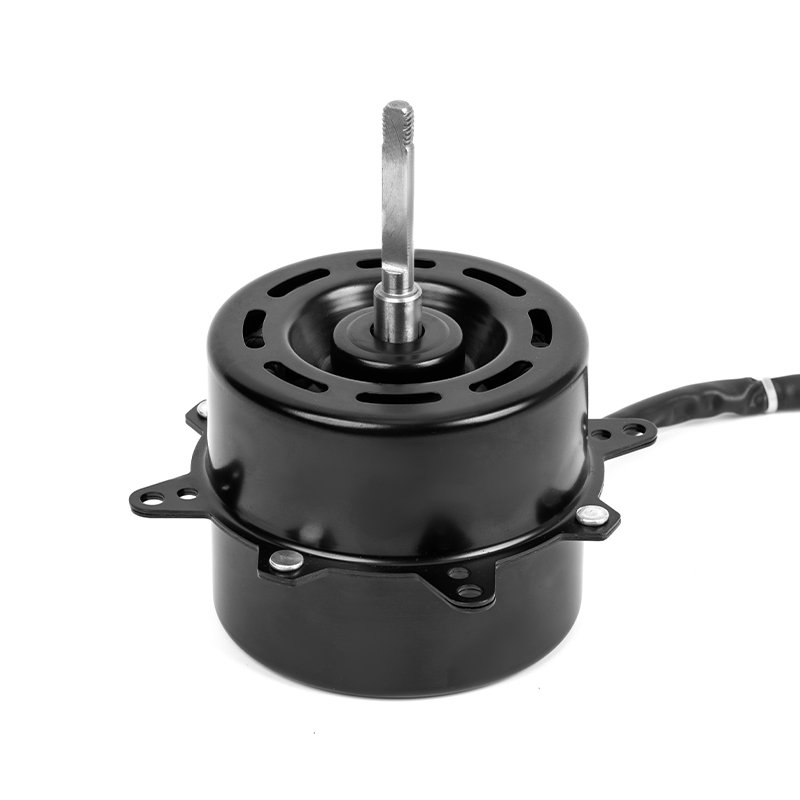
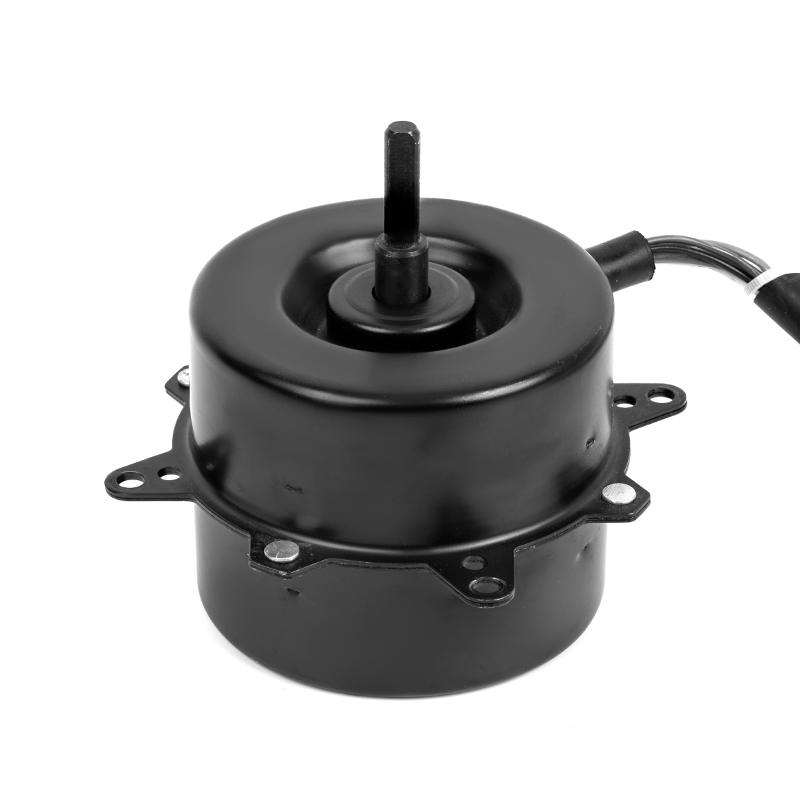
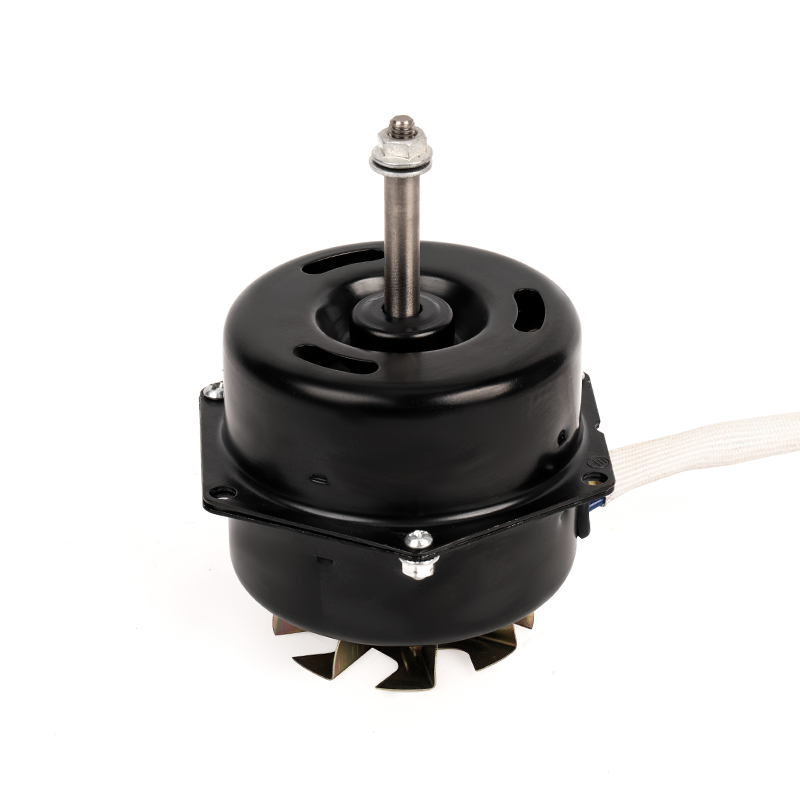
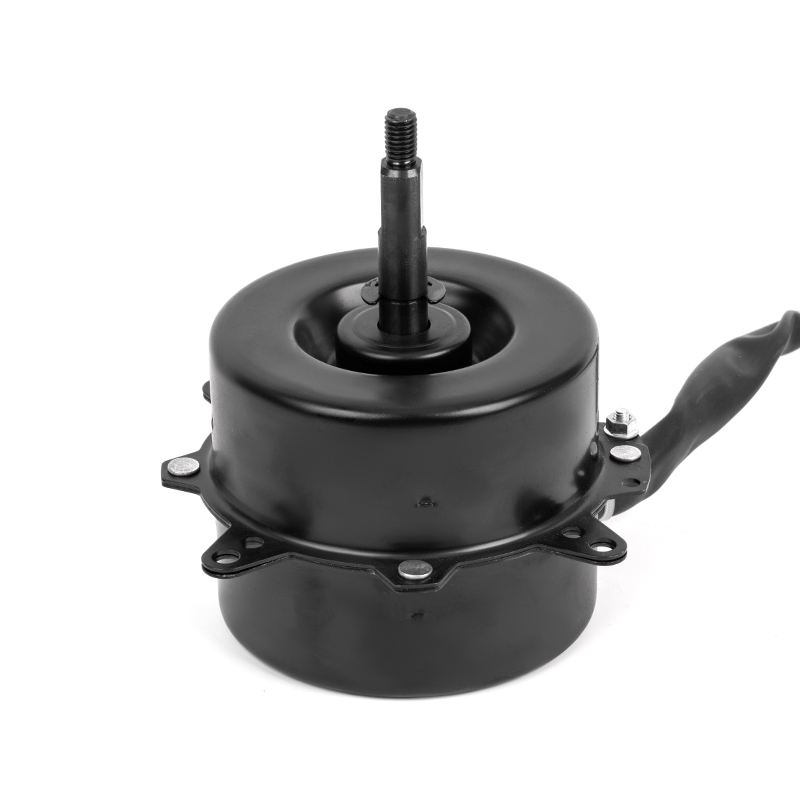
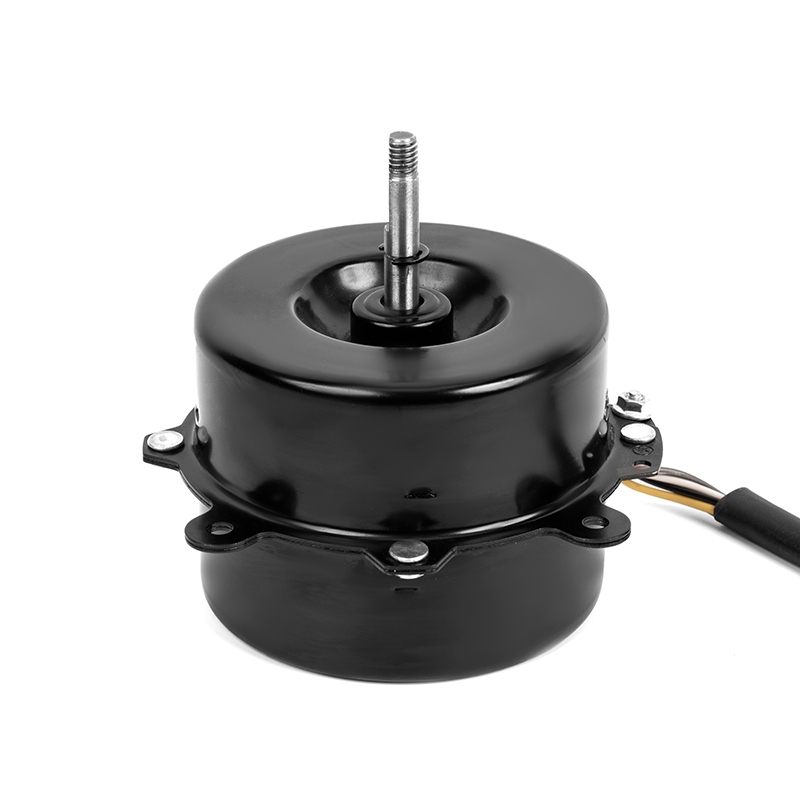
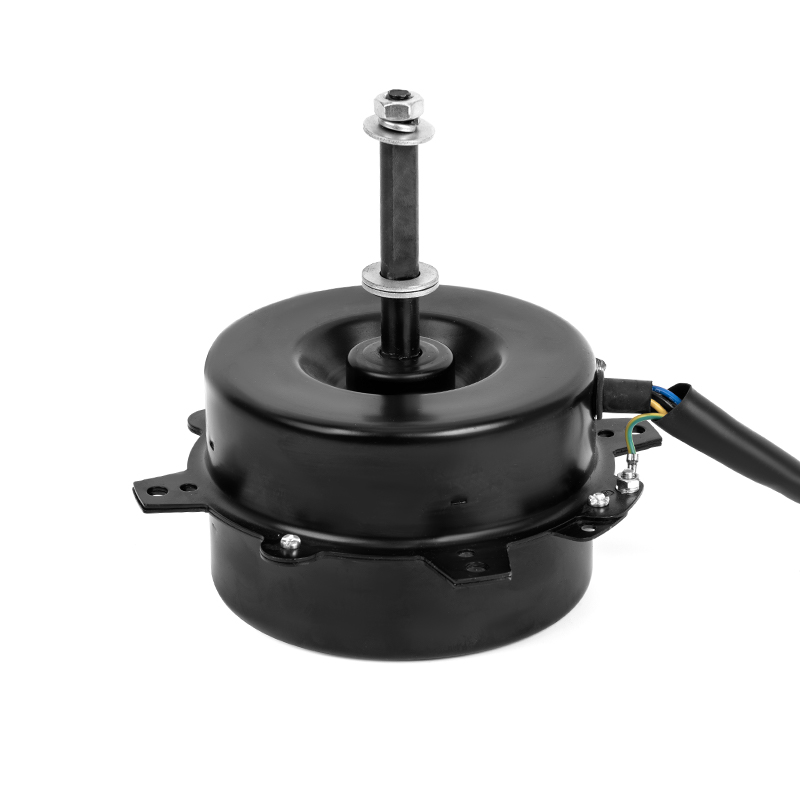
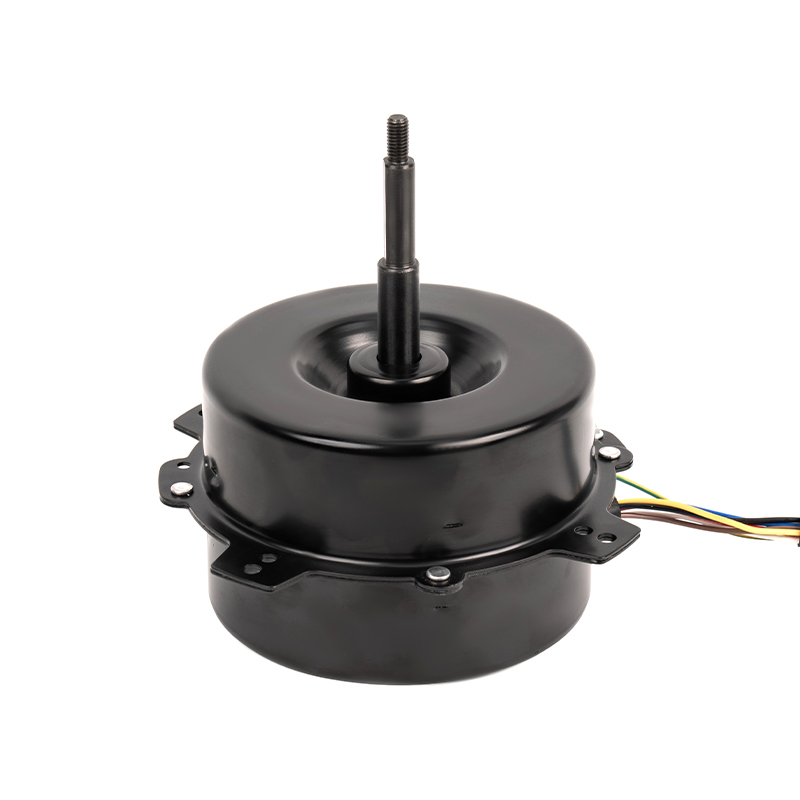
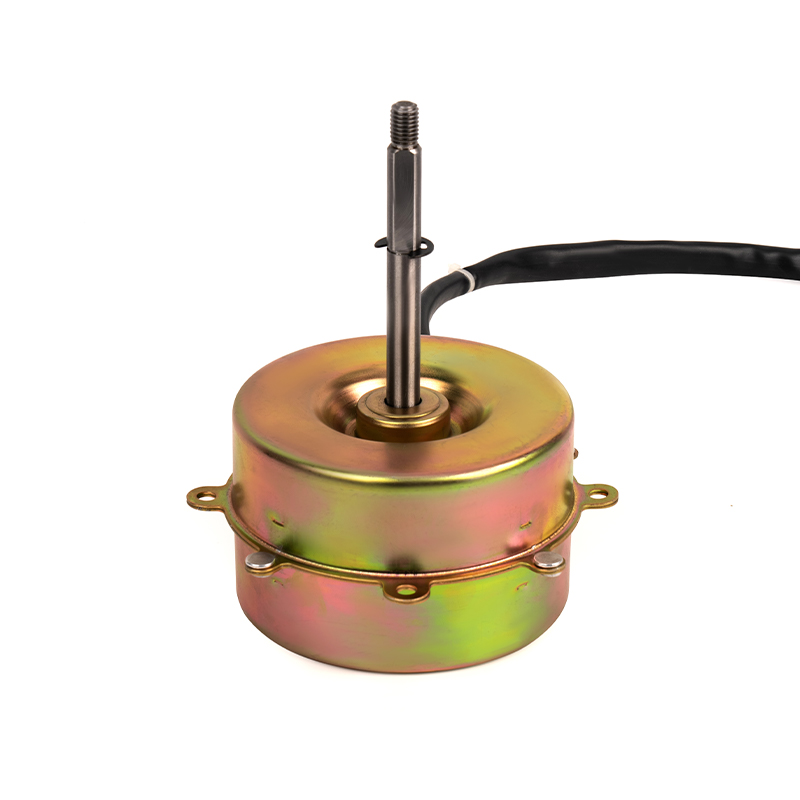
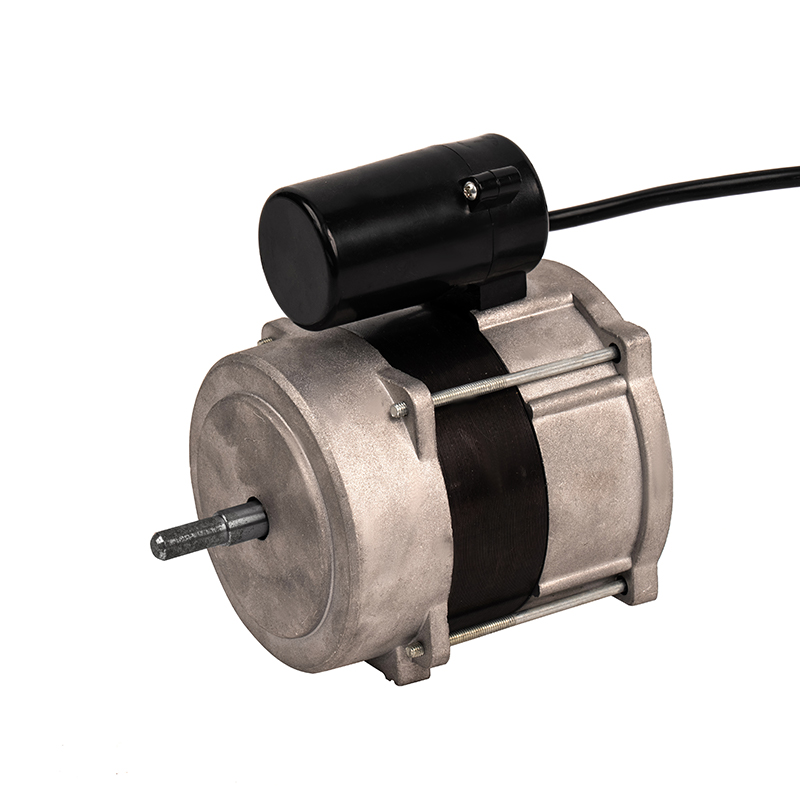
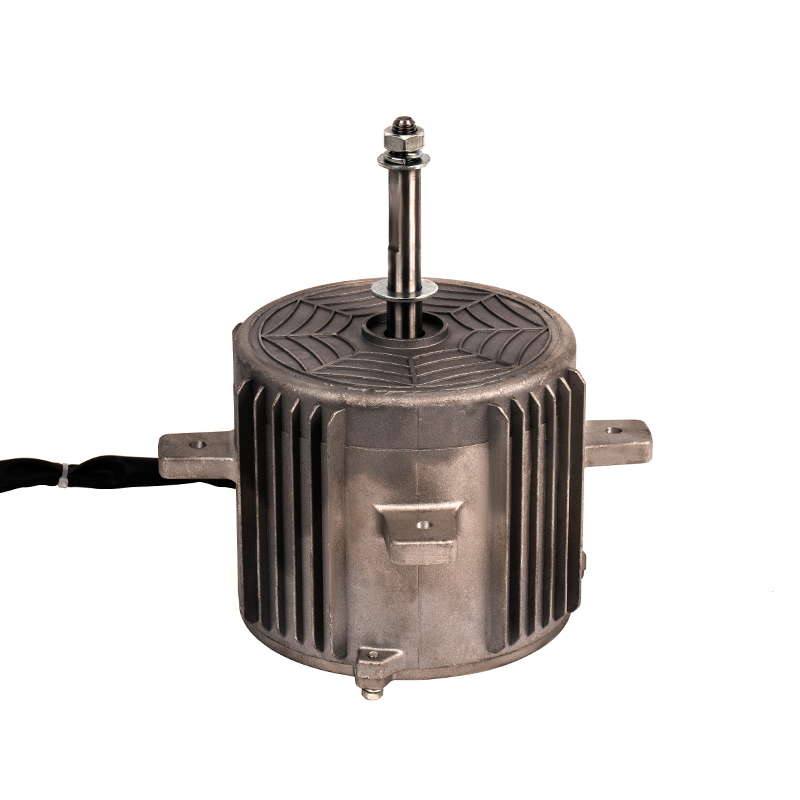
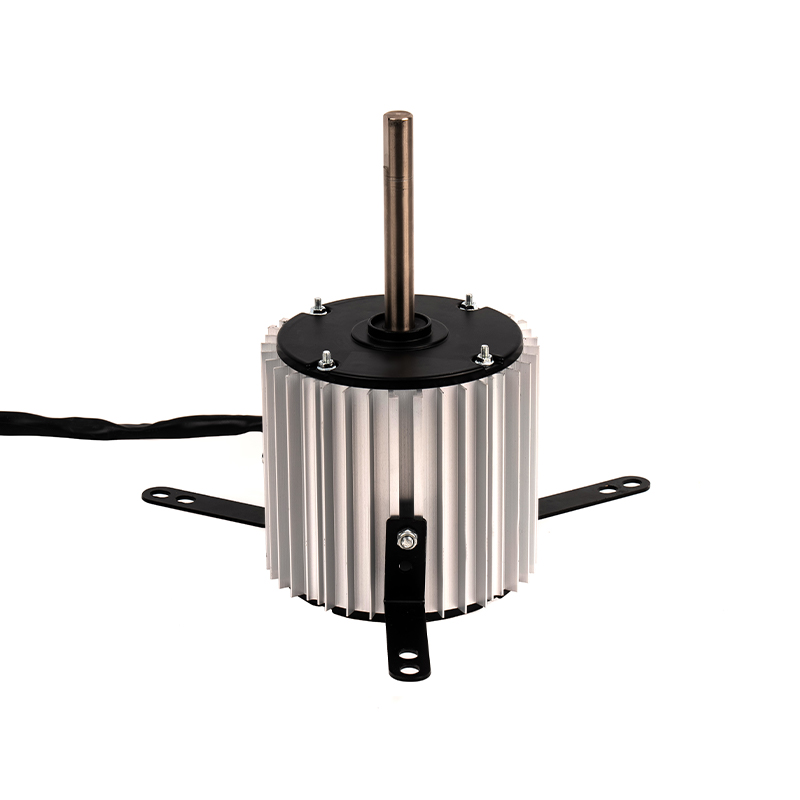
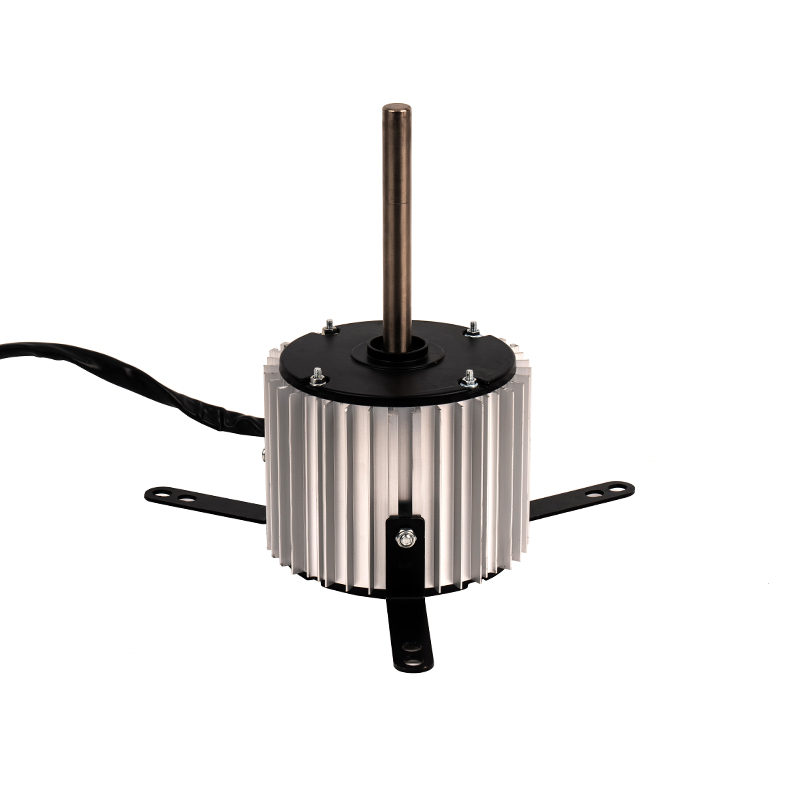
A DC Motor is a direct current motor. The commutator and brushes, one of its core components, are the key to the smooth operation of the motor. The precise coordination between them ensures that the motor can work continuously and efficiently.
The commutator is a precision device inside a DC motor. It is exquisitely designed and powerful. As the motor rotates, the multiple commutator segments on the commutator contact the brushes in turn. This dynamic process realizes the periodic change of the direction of the current in the armature winding. This change is based on the basic principle of electromagnetism, that is, the current is subjected to force in the magnetic field, and the direction of the force depends on the direction relationship between the current and the magnetic field. Through the action of the commutator, the direction of the current can be adjusted in time, thereby ensuring that the armature is always subjected to the force that drives it to rotate in the magnetic field, realizing the continuous rotation of the motor.
As a bridge connecting the power supply and the armature winding, the importance of brushes is self-evident. They are made of highly conductive and wear-resistant materials, such as graphite or copper-graphite composites, to ensure good conductivity and stability under high-speed rotation and frequent contact. The brushes maintain close contact with the commutator through springs or other elastic devices, stably transmitting the DC power in the power supply to the rotating armature winding. At the same time, the brushes also assume a certain mechanical support role, ensuring that the commutator will not be damaged by centrifugal force or vibration when rotating at high speed.
The coordinated work of the commutator and the brushes is the key to the stable and efficient operation of the DC motor. The precise coordination between them not only ensures the timely change of the current direction, but also ensures the stable operation of the motor under various working conditions.


 English
English عربى
عربى ++86 13524608688
++86 13524608688












