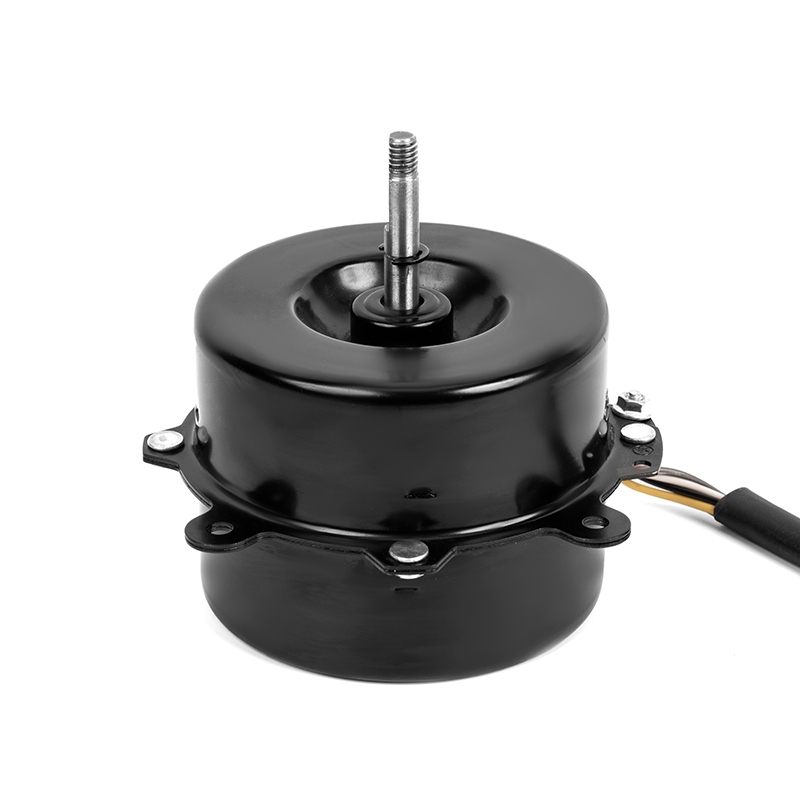
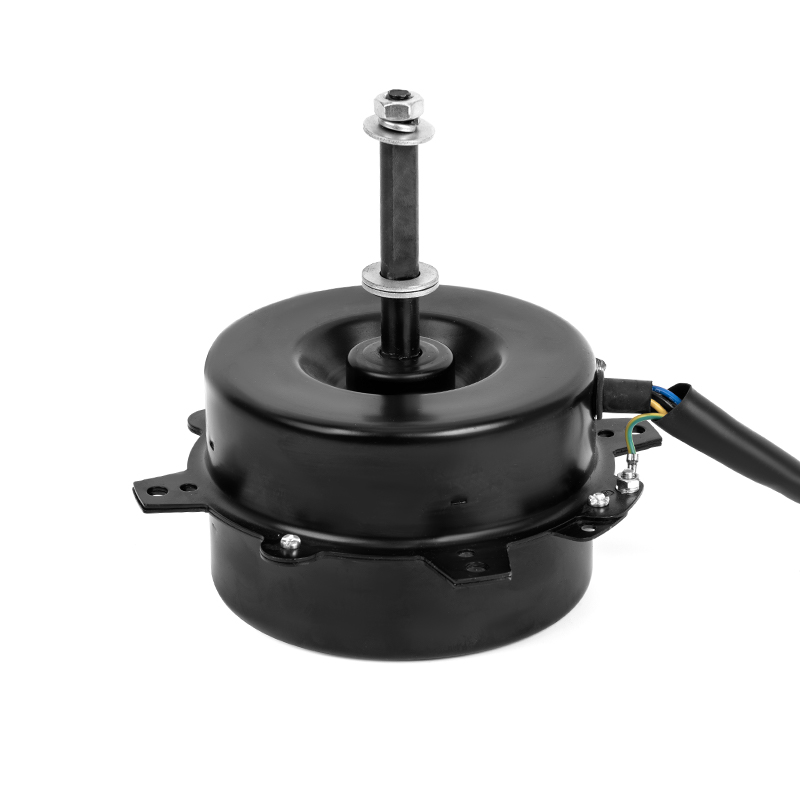
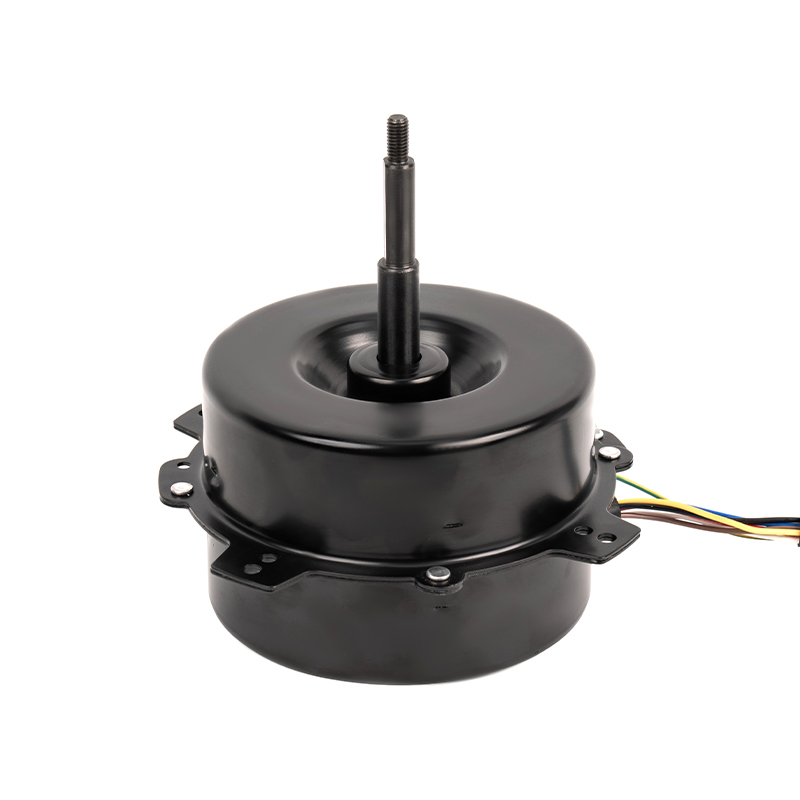
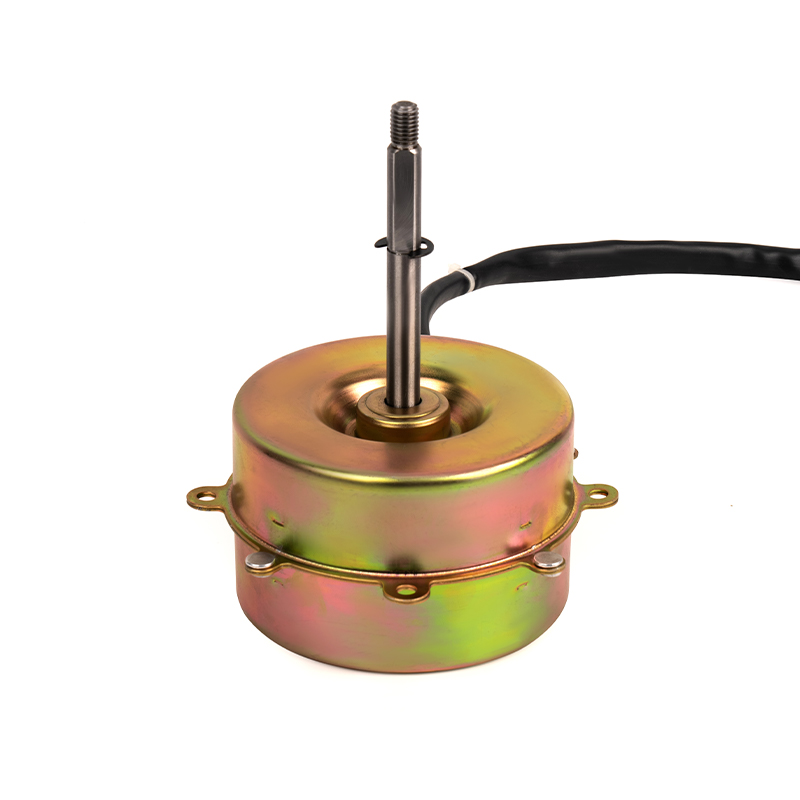
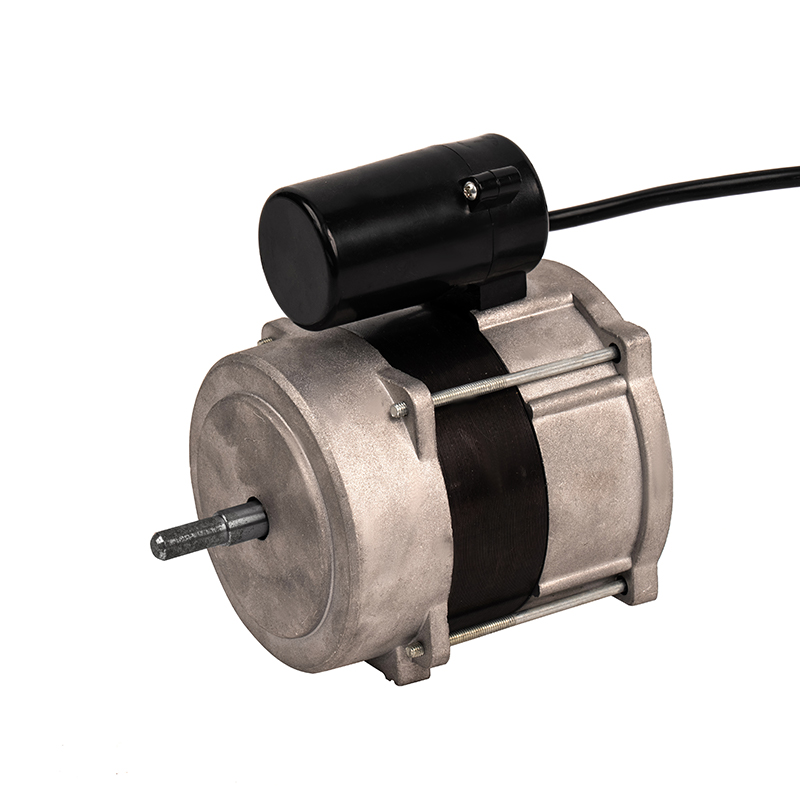
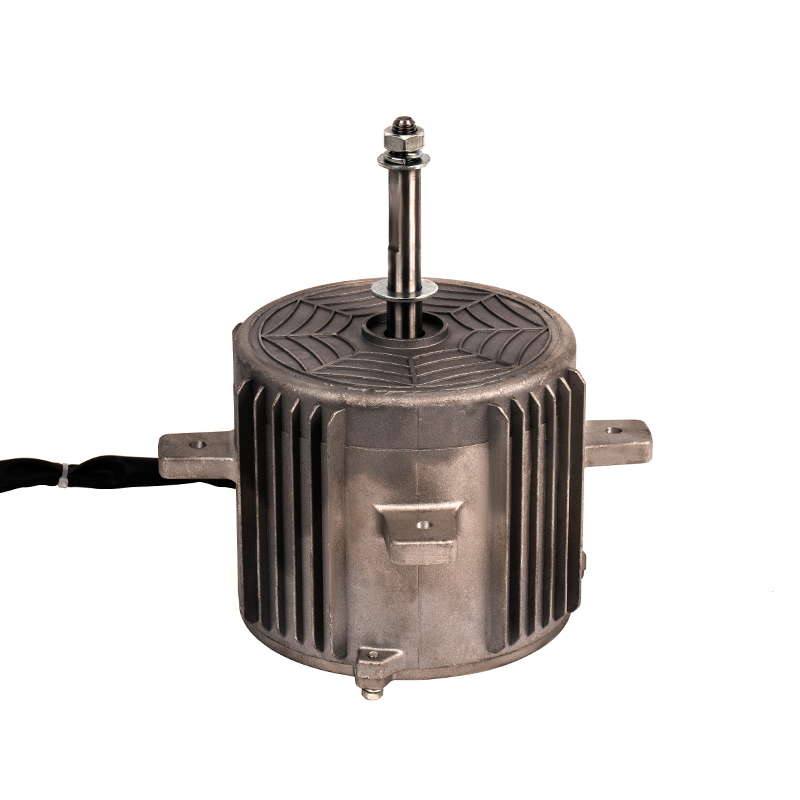
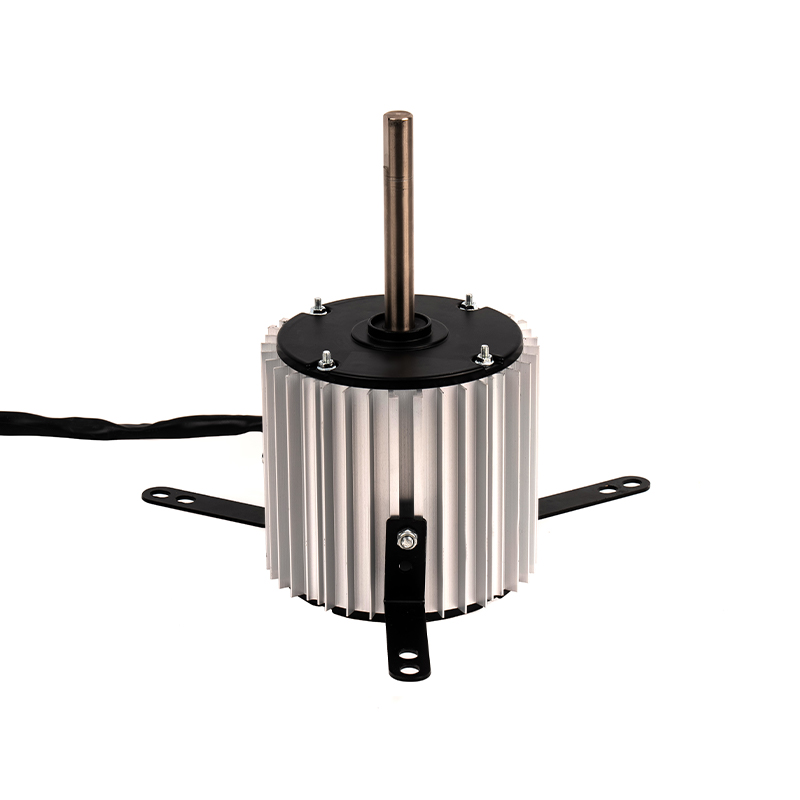
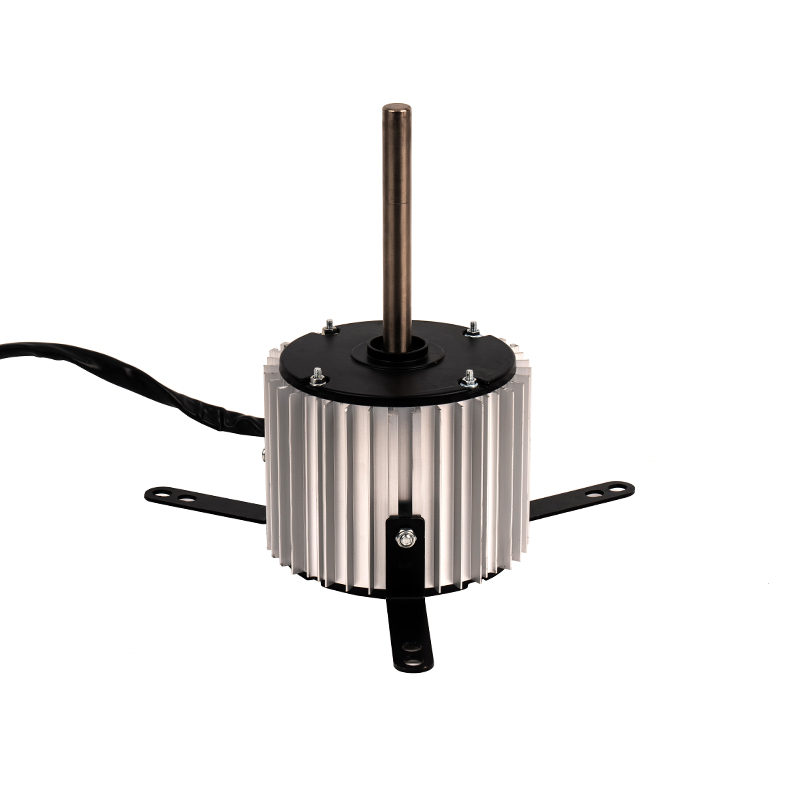
One of the most significant advantages of plastic asynchronous motors is their lightweight nature compared to traditional metal motors. Plastic components are inherently lighter than metal, which reduces the overall weight of the motor. This reduction can translate into improved energy efficiency for equipment, as less power is required to move or operate lighter systems. Lighter motors are easier to handle during installation, repair, or maintenance, reducing the need for heavy-duty lifting equipment and minimizing the risk of injury during manual handling. The lower weight can also reduce shipping and transportation costs, especially in large-scale industrial operations where equipment is regularly moved or exported.
Plastic materials are naturally resistant to corrosion, which is a common problem in many industrial environments where metal components are exposed to moisture, chemicals, or other corrosive substances. In industries such as marine, chemical processing, and food and beverage production, corrosion can significantly reduce the lifespan of metal motors and lead to costly downtime due to frequent repairs or replacements. Plastic asynchronous motors are ideal for such environments, as they can operate in harsh conditions without degrading. This corrosion resistance enhances the longevity of the motor, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and providing a more reliable solution over time.
From a cost perspective, plastic asynchronous motors offer notable advantages. The manufacturing process for plastic components, such as injection molding, is generally more economical than metal fabrication techniques like casting or machining. Plastic materials are often less expensive than metals such as steel or aluminum, resulting in lower production costs. Additionally, the reduced weight of plastic motors can decrease operational energy costs, leading to savings over the lifetime of the motor. For businesses aiming to optimize their budget while maintaining high performance, plastic asynchronous motors provide a cost-effective alternative without sacrificing functionality or durability.
One of the inherent properties of plastic is its superior electrical and thermal insulation. Unlike metals, which are conductive, plastics do not conduct electricity, reducing the risk of electrical shorts or failures in environments where motors are exposed to moisture or conductive materials. This makes plastic asynchronous motors safer for use in applications where electrical safety is a concern. Furthermore, plastic materials can withstand higher temperatures without degrading, providing better thermal stability. This makes plastic motors less susceptible to overheating, which can be a major issue in high-demand industrial applications where motors are required to run continuously for long periods.
Noise pollution is a common issue in many industrial settings, especially where metal motors are used. Plastic asynchronous motors have the advantage of producing less noise due to the inherent vibration-dampening properties of plastic. Plastics are better at absorbing vibrations than metals, which results in quieter motor operation. In environments such as laboratories, hospitals, or office settings, where noise control is important, plastic motors can help create a quieter workspace. This also enhances the comfort of employees working around the machinery and helps companies comply with noise regulations in sensitive industrial or commercial environments.


 English
English عربى
عربى ++86 13524608688
++86 13524608688












