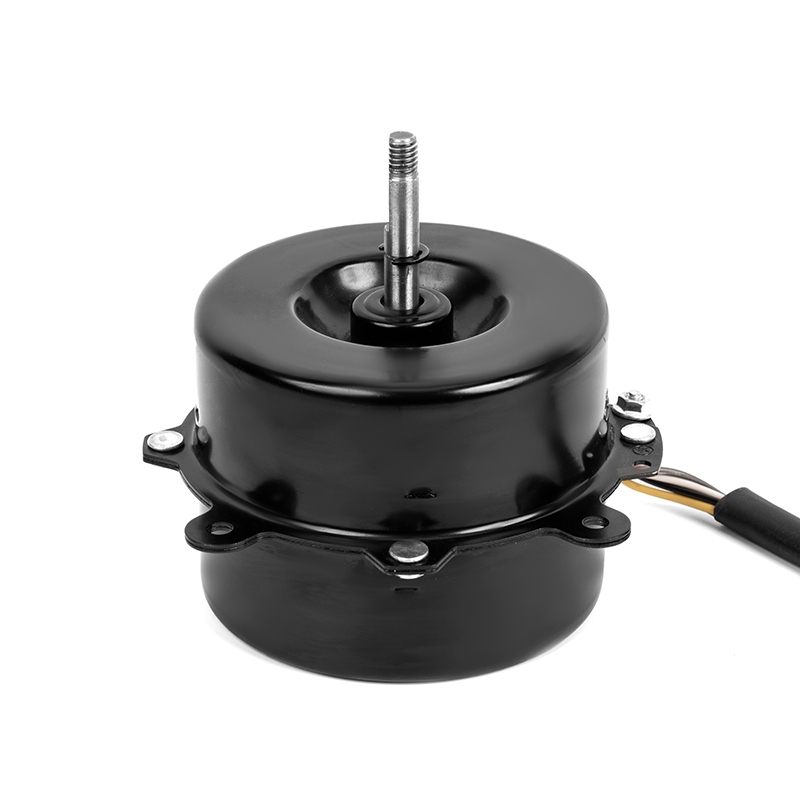
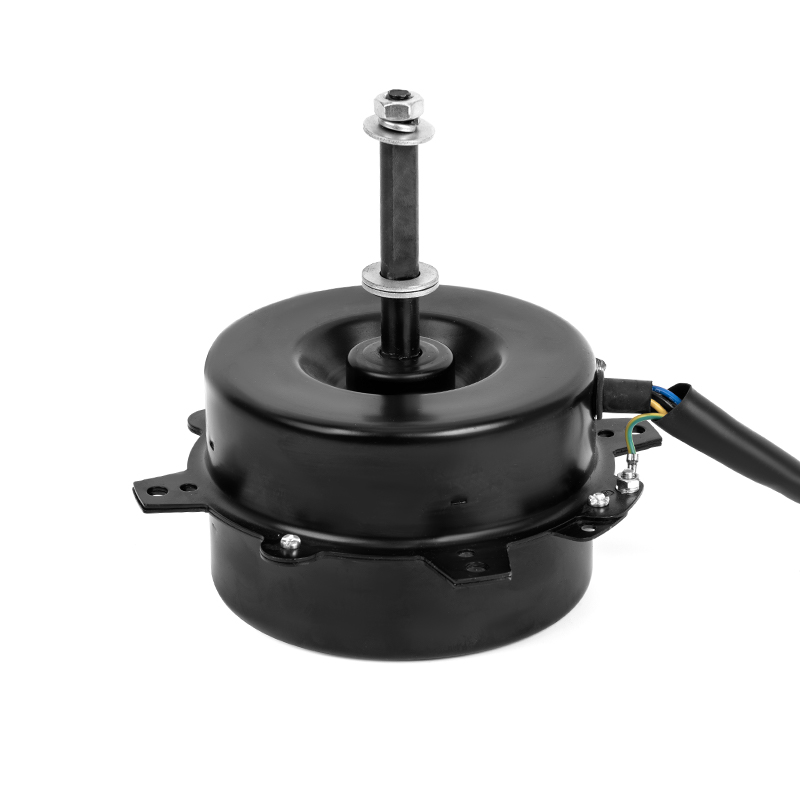
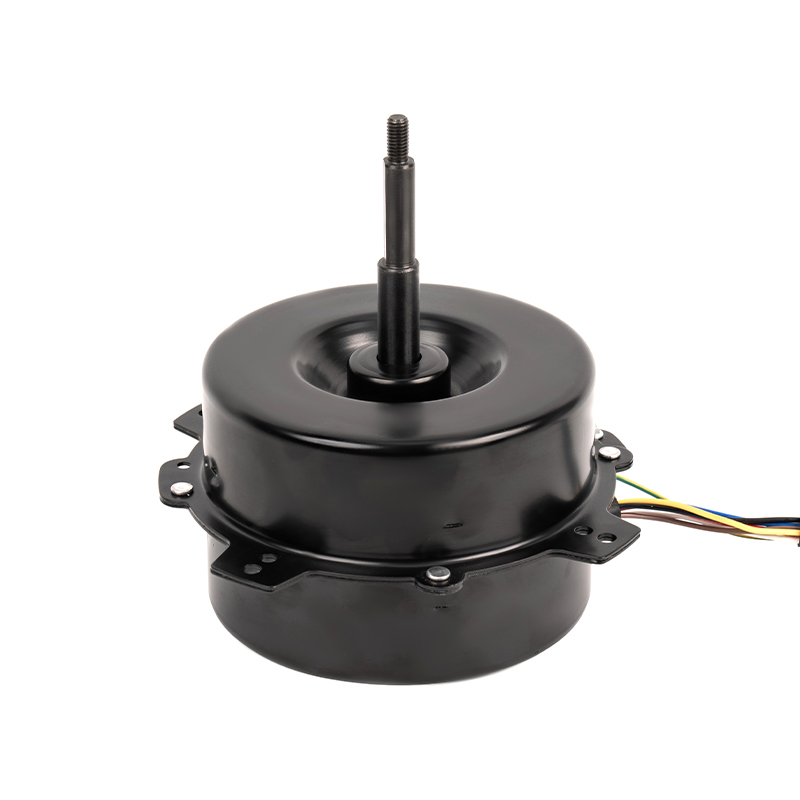
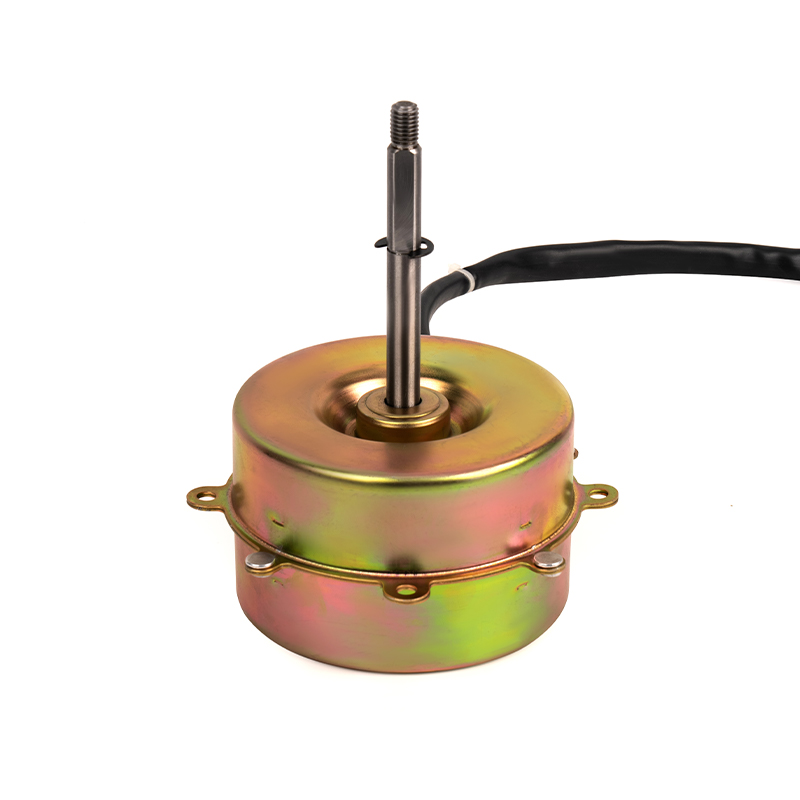
Energy Consumption and Cost: The efficiency of a mobile air conditioning motor is a critical factor in determining the overall energy consumption of the unit. An efficient motor is designed to convert a higher percentage of electrical energy into useful mechanical energy, which directly contributes to the cooling process. This conversion efficiency minimizes energy losses in the form of heat, which is prevalent in less efficient motors. For example, a motor with an efficiency rating of 90% will convert 90% of electrical power into cooling energy, with only 10% lost as heat. This enhanced energy conversion capability means that the motor requires less power to achieve the same cooling effect as a less efficient motor. Consequently, the overall electrical demand of the air conditioning system is reduced. Lower power consumption directly translates to reduced utility bills, offering significant cost savings over time. For instance, if an inefficient motor increases the power consumption of a system by 20%, a more efficient motor can mitigate this increase, leading to substantial reductions in electricity costs.
Heat Generation: In less efficient motors, a significant portion of electrical energy is lost as heat due to factors such as higher internal resistance, friction, and other mechanical inefficiencies. This excess heat generated by the motor is then transferred to the surrounding environment, increasing the ambient temperature around the air conditioning unit. As a result, the air conditioning system must work harder to maintain the desired temperature, compensating for the additional heat load. This increased operational demand leads to higher energy consumption as the system strives to remove the extra heat. In contrast, an efficient motor generates less heat due to its optimized design, which reduces electrical resistance and mechanical friction. By minimizing waste heat, the efficient motor alleviates the additional cooling load on the air conditioning system. This reduction in the thermal burden allows the system to operate more efficiently, reducing the overall energy required to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures.
Operational Longevity: The operational efficiency of a motor is closely linked to its longevity. High-efficiency motors are engineered to operate under optimal conditions, which reduces the strain on internal components. This optimized performance minimizes wear and tear on the motor, leading to extended operational lifespans. Efficient motors typically feature high-quality bearings, advanced cooling mechanisms, and superior materials that contribute to their durability. Extended motor lifespan means fewer replacements and maintenance interventions are required. This not only reduces the direct costs associated with purchasing new motors but also decreases the frequency of service calls and associated labor costs. The longer-lasting motor contributes to reduced environmental impact by minimizing waste and the consumption of resources needed for manufacturing and disposal.
System Compatibility: Modern air conditioning systems are often designed with a focus on energy efficiency, incorporating advanced technologies such as variable speed drives, smart thermostats, and high-efficiency compressors. A high-efficiency motor is designed to integrate seamlessly with these advanced systems, enhancing overall performance and energy efficiency. By matching the motor's efficiency with the system's design, the entire unit operates in a more cohesive manner, maximizing cooling effectiveness while minimizing energy consumption. This compatibility ensures that the motor works in harmony with other system components, such as the evaporator and condenser coils, to deliver optimal cooling performance with reduced energy usage.
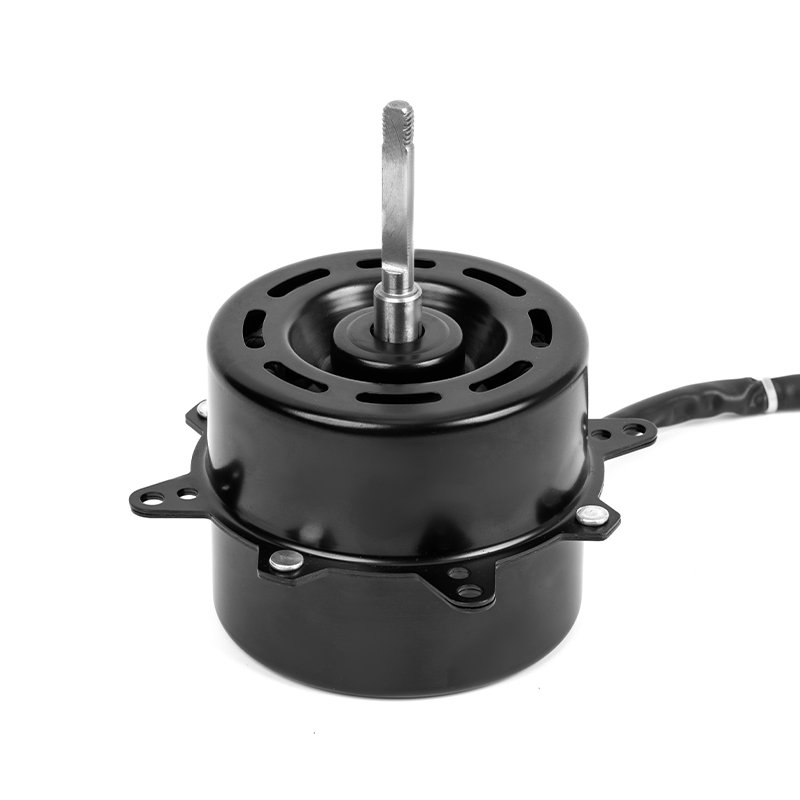
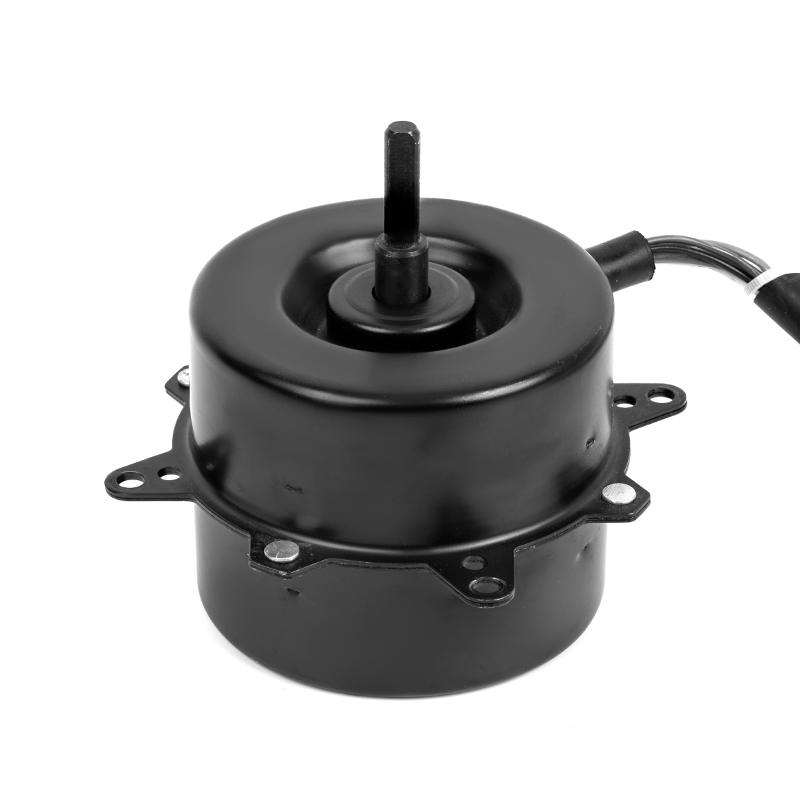
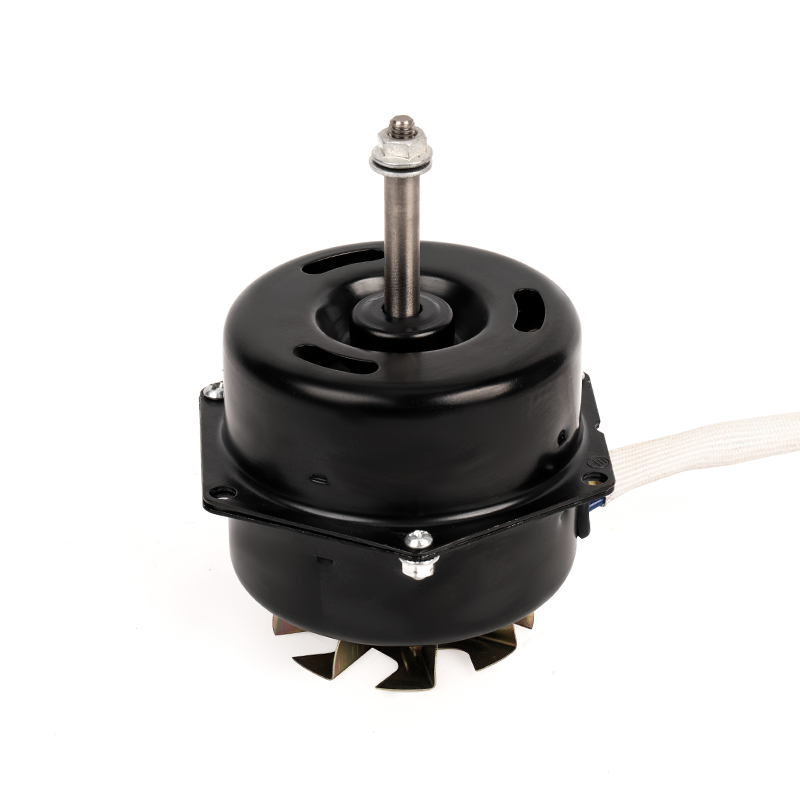
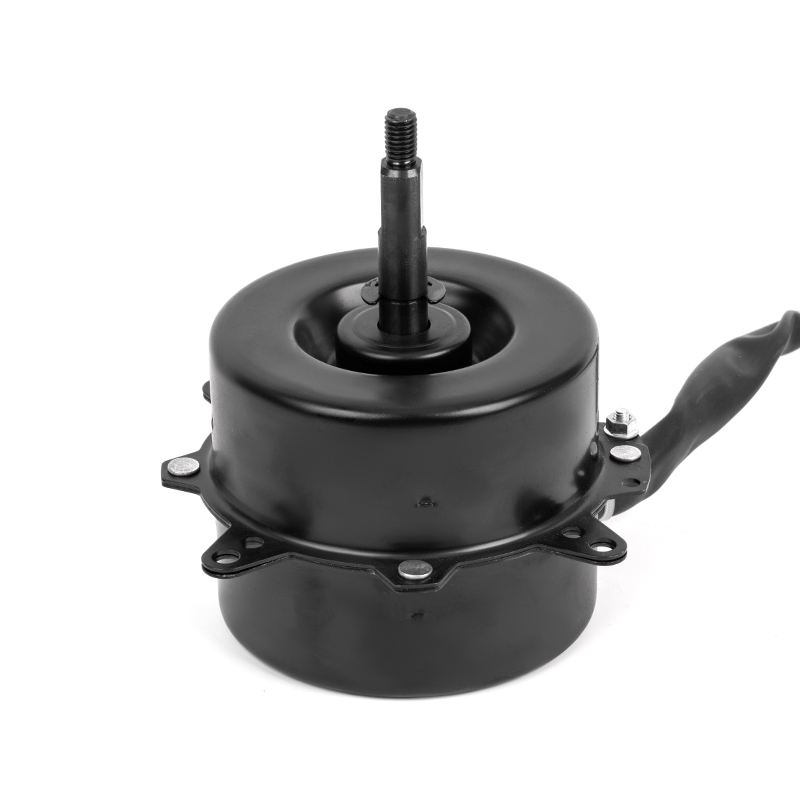
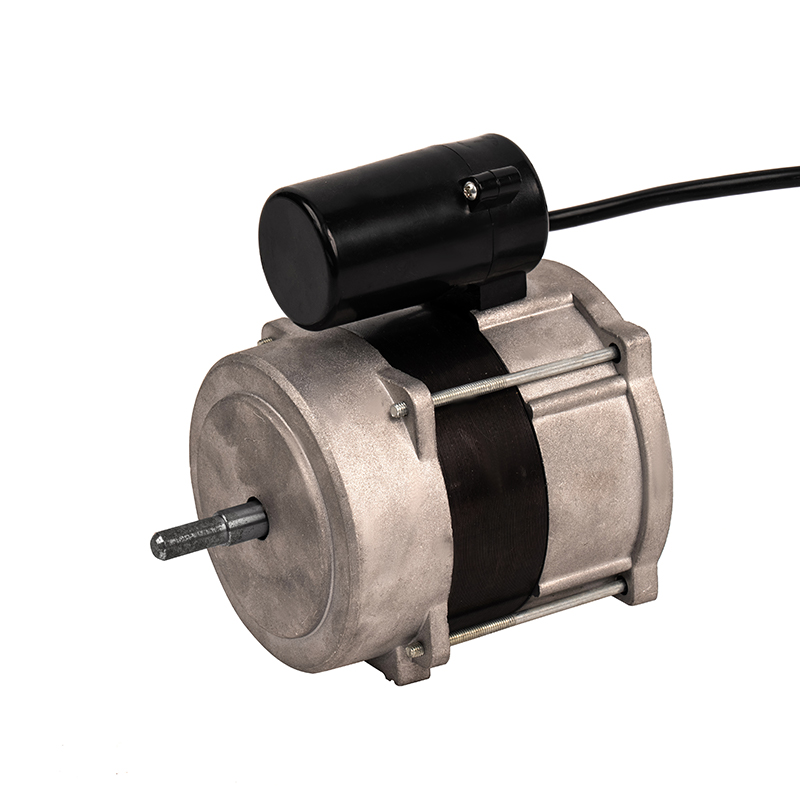
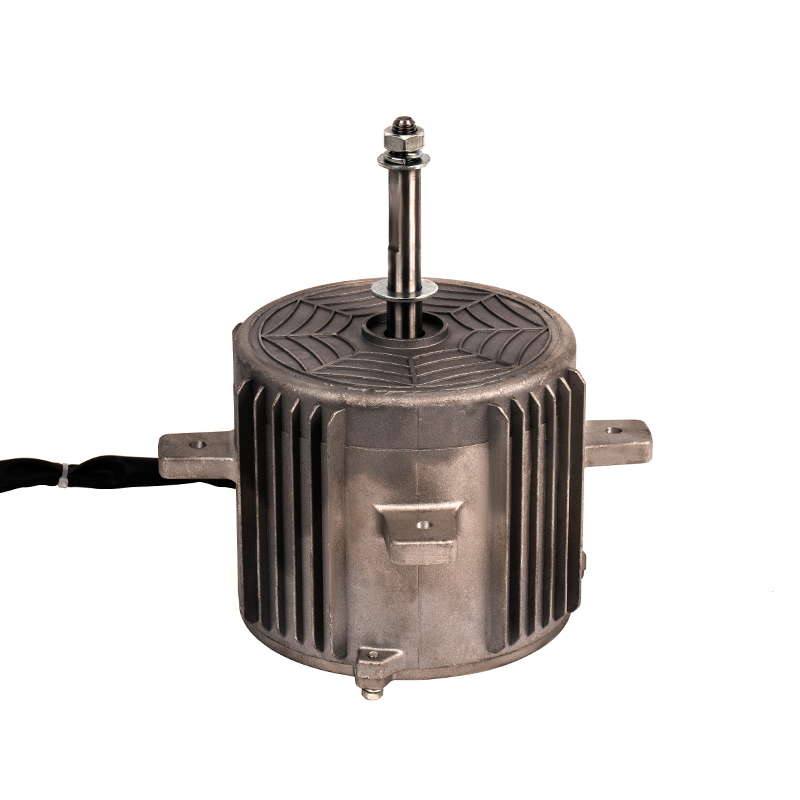
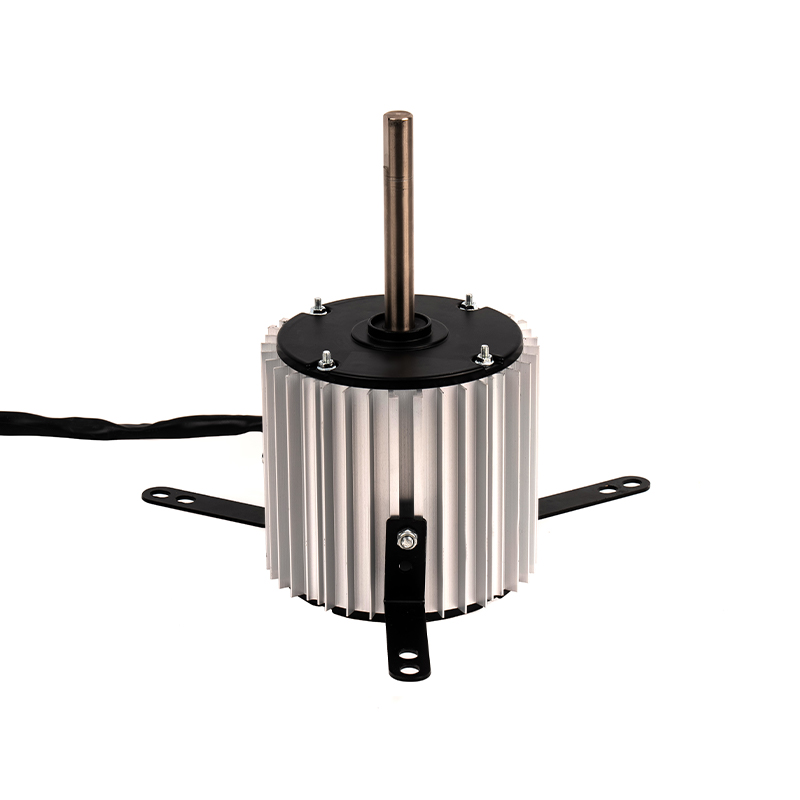
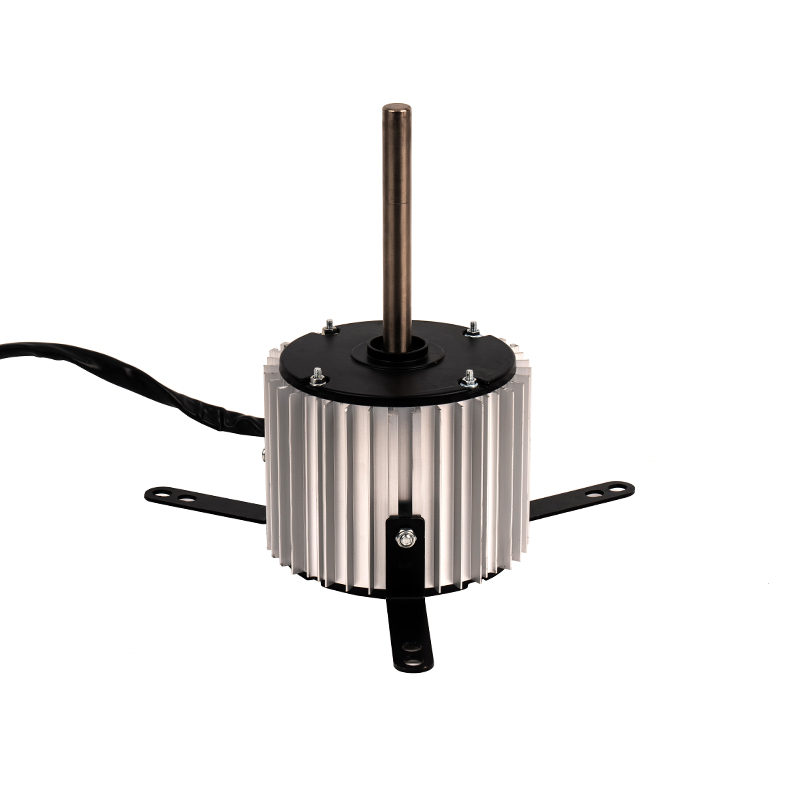
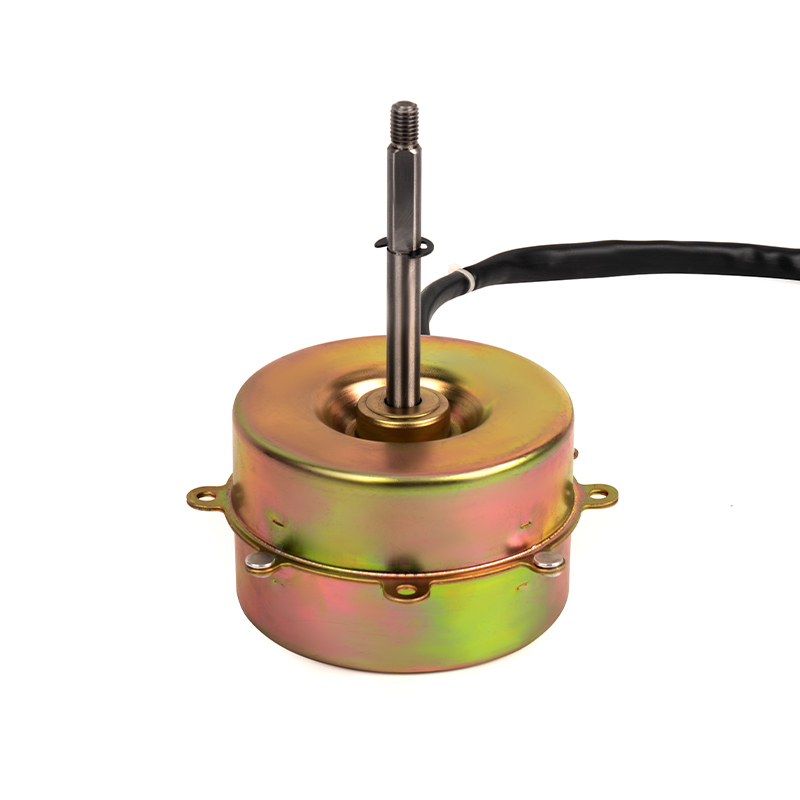
YSY-120(618T) Color Gold Single-Phase Cold Air AC Motor



 English
English عربى
عربى ++86 13524608688
++86 13524608688












