The motor’s plastic encapsulation is engineered to create a robust barrier against external contaminants, including moisture and oil. This encapsulation is typically crafted from high-performance polymers that exhibit excellent resistance to both chemical and environmental stressors. The plastic casing fully encloses the motor's internal components, such as the stator, rotor, and windings, shielding them from direct exposure to oil fumes and moisture. This protective barrier significantly reduces the risk of electrical failures, such as short circuits, that can occur when these elements come into contact with conductive fluids. By preventing ingress of moisture and oil, the encapsulation helps in maintaining the integrity and longevity of the motor’s internal components, ensuring sustained performance in challenging environments.
The motor is typically designed with precision-sealed bearings and joints, which are crucial for preventing the intrusion of oil and moisture. These seals are made from materials that are specifically chosen for their durability and resistance to oil and water. The sealed design ensures that even in environments with high concentrations of oil fumes or humidity, the motor’s critical components remain uncontaminated. This is particularly important for maintaining the smooth operation of moving parts, such as bearings and shafts, which can be adversely affected by the presence of oil and moisture. The seals also contribute to reducing the need for frequent maintenance, as they minimize the wear and tear that can result from the penetration of contaminants.
The encapsulation materials used in the motor are selected for their inherent resistance to corrosion, which is essential in environments where oil fumes and moisture are prevalent. Corrosion can lead to the degradation of metallic components, resulting in a loss of structural integrity and a decrease in the motor’s operational efficiency. By using corrosion-resistant polymers and coatings, the motor is better equipped to withstand prolonged exposure to corrosive elements without compromising its functionality. This resistance not only extends the motor's operational life but also ensures consistent performance over time, even in the harshest conditions.
Some advanced motor designs incorporate self-cleaning mechanisms or use materials that inherently resist the accumulation of oil and moisture. For instance, the encapsulation may have a non-stick surface that prevents oil from adhering to the motor’s exterior, or it might include hydrophobic properties that repel water. These features help to minimize the buildup of contaminants, which can otherwise lead to overheating, reduced efficiency, or mechanical failure. By reducing the adherence of oil and moisture, the motor maintains its cooling efficiency and reduces the likelihood of overheating, thus enhancing its overall reliability and performance.
While the motor is designed to be robust and resistant to moisture and oil buildup, regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Maintenance practices may include periodic inspections of the seals and encapsulation to check for any signs of wear or damage. Cleaning the exterior of the motor to remove any accumulated oil or debris is also recommended. Ensuring that ventilation and drainage systems (if present) are functioning properly can help prevent the buildup of moisture and oil within the motor. Adhering to a regular maintenance schedule will help in early detection of potential issues, allowing for timely interventions that can prevent costly repairs or downtime.
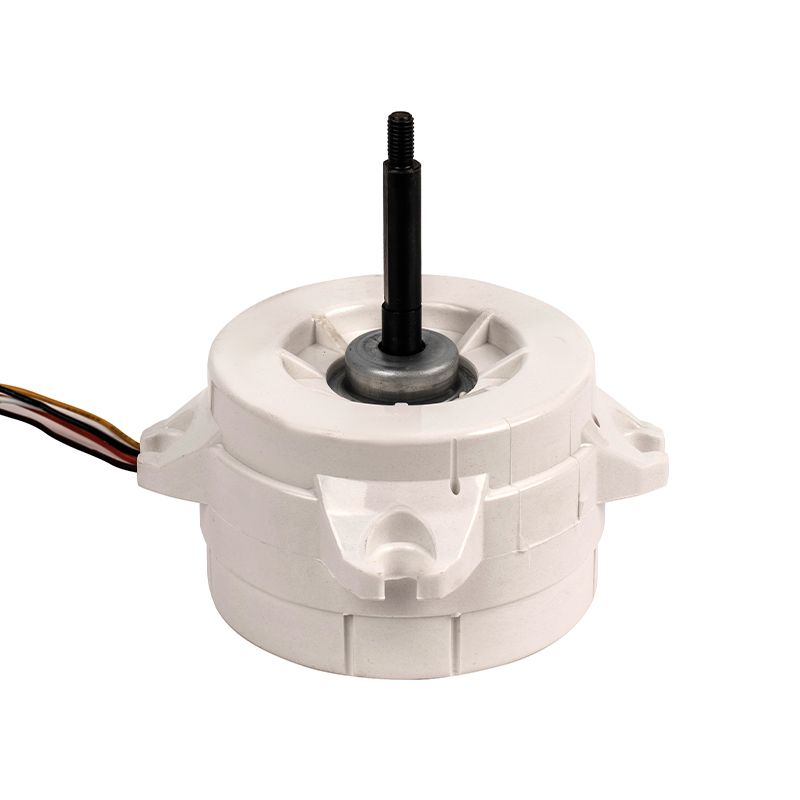
YYS80-4 Plastic Single-Phase Asynchronous Motor
 https://www.coolingfanmotor.com/product/plastic-encapsulated-oil-fume-ac-motor/yys804-plastic-singlephase-asynchronous-motor.html
https://www.coolingfanmotor.com/product/plastic-encapsulated-oil-fume-ac-motor/yys804-plastic-singlephase-asynchronous-motor.html


 English
English عربى
عربى ++86 13524608688
++86 13524608688












